Tendonitis
Shoulder dislocation results when the top of the arm bone, the humerus, detaches from the shoulder blade, or the scapula.
Bursitis
Bursitis is painful inflammation of the bursae, the fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles. Bursitis in the shoulder is commonly caused by an injury, infection or other condition. Pain may be accompanied by swelling, tenderness or loss of movement. Treatment is rest, ice, activity modifications, injections, and in some cases, surgery.
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)
Tennis elbow is caused by the overuse of the forearm, hand and other arm muscles, causing injury to the tendons on the outside area of the elbow. Symptoms include pain on the outside of the elbow that may also be present in the forearm and wrist, which worsens with activity (such as shaking hands, lifting objects, and opening jars). Although this is common in tennis players, anyone who performs repetitive arm and wrist motions may develop tennis elbow, or tendinopathy. Treatment is rest, ice, activity modifications, injections, and in some cases, surgery.
Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis)
Similar to tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow (or medial epicondylitis) is caused by overusing the forearm muscles through repetitive gripping, swinging (such as in golf), or flexing, which causes damage to the tendons (tendonitis) near the elbow. Pain from golfer’s elbow generally occurs on the inside of the elbow and down into the forearm. Treatment is rest, ice, activity modifications, injections, and in some cases, surgery.
Little league elbow (pitcher’s elbow)
Little league elbow (also known as pitcher’s elbow or medial apophysitis) is an overuse injury that affects children and adolescents involved in sports that require a repetitive throwing motion, such as pitching in baseball. Symptoms include pain, swelling and restricted motion.
Cubital tunnel syndrome
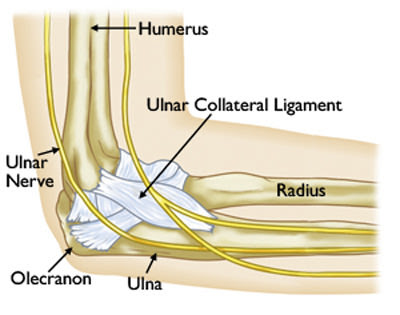
Cubital tunnel syndrome, also known as ulnar neuropathy, is the compression or irritation of the ulnar nerve, which runs through the groove along the medial side of the elbow (in the area commonly referred to as the funny bone). Cubital tunnel symptoms include pain, numbness, and muscle weakness. Treatment includes anti-inflammatory medications, splinting, activity modifications, and in some cases surgery.
Osteochondritis dissecans
Osteochondritis dissecans occurs in children and adolescents when a piece of bone or cartilage inside a joint loses blood supply. This causes a piece of the cartilage, and usually a thin layer of bone beneath it, to separate and sometimes fall into the joint space. Symptoms commonly include pain, swelling, and problems moving the affected joint. Treatment includes rest, and when it is not healing properly, surgery.
Fractures
A fracture is a break in a bone. Broken bone symptoms include pain (intensified when the area is moved or pressure is applied), swelling, bruising, and loss of function. Fractures may also cause the area around the bone to appear distorted or deformed, especially in open fractures where the bone protrudes from the skin.
A stress fracture is a hairline crack in a bone that can worsen during activity over time. Stress fracture symptoms include pain, which increases with activity and decreases after rest, in addition to swelling and tenderness.
Arthritis
Arthritis, or osteoarthritis, is loss of cartilage within a joint. While there are many other types of arthritis, including rheumatoid, psoriatic, septic, post-traumatic, and lupus, wear and tear osteoarthritis remains by far the most common. Arthritis symptoms can include swelling, tenderness, sharp pain, stiffness, and sometimes fever and chills.
Bone spurs
Bone spurs (also known as osteophytes) are bony projections that develop on the surface of the bone, and are often the result of osteoarthritis. Bone spurs usually do not cause symptoms, but can cause swelling, pain, and tearing to the surrounding tissue or tendon. Corns or calluses may also build up over time to provide padding in the area of the bone spur.
Dislocation
Elbow joint dislocation occurs when the forearm bones (the radius and ulna) move out of alignment with the upper arm bone (the humerus). This is generally the result of trauma. Elbow dislocation is accompanied by swelling, pain, and inability to bend the arm at the elbow. Treatment involved reduction, immobilization, physical therapy, and in some cases surgery.
Ruptured biceps tendon
The tendon connecting the biceps muscle to the radius may encounter too much force and rupture, leading to pain and a bulging deformity in the arm. It is most often caused by a sudden injury in which heavy weight is resisted by elbow flexion. This injury causes weakness in both elbow flexion and forearm rotation. Surgery is often required to regain full strength.